Year: 2024
How Do Vitamins Work? The Science Behind Their Absorption
Many of the foods we eat naturally contain vitamins and other nutrients, while others are fortified, such as milk with added vitamin D. Still, some people lack certain essential vitamins due to their diet, age, gender, genetics or other factors. To compensate, many take supplements, such as multivitamins, that deliver a variety of vitamins and minerals in every dose.
How do vitamins work in the body? Let’s explore this topic and examine the ongoing controversy surrounding supplement efficacy within medical and scientific communities.
How Do Vitamin Supplements Travel Through Your Body?
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how vitamins travel through the human body:
- You swallow the vitamin supplement, and it moves down the esophagus to the stomach.
- In the stomach, digestion begins. Digestive acids and enzymes begin to dissolve the supplement, but it’s not fully digested here.
- The remaining portion travels to the small intestine, where it’s further broken down by digestive enzymes and fluids from the liver and pancreas.
- In the second and third parts of the small intestine, nutrients from the digested supplement are absorbed into the intestinal lining. From here, the method of entry into the bloodstream depends on the type of vitamin:
- Water-soluble vitamins (B and C) are absorbed directly into the bloodstream.
- Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K) must be broken down by bile acids before being absorbed. These are then absorbed by the lymphatic system and transported into the bloodstream.
- The bloodstream carries the beneficial portions of the vitamin to various cells and tissues in the body.
- Excess water-soluble vitamins and their byproducts exit the body through urine, while remaining fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the liver and fatty tissues for later use.
What Is the Role of Vitamins in Our Bodies?
Vitamins play crucial roles throughout the body, aiding each organ, tissue and cell in different ways. They help:
- Fight infections
- Improve vision
- Build strong bones and muscles
- Regulate hormones
Many cells in our bodies, from skin to bone, regenerate regularly to replace old and damaged ones. For example, the outer layer of our skin cells renews about once a month. This regeneration process requires vitamins, whether obtained from food or supplements, making them essential to the normal, healthy functioning of the body.
What’s the Controversy Behind Vitamin Supplements?
While taking vitamin supplements may seem beneficial, many experts argue that vitamins in supplement form provide little to no health value compared to those obtained through food. Some point to scant evidence that supplements prevent or cure any major diseases.
Others contend that the body does absorb beneficial vitamins from supplements but eliminates excess amounts through urination — a potentially favorable scenario. Most experts agree that the best way to obtain vitamins is through a nutrient-rich diet rather than supplements.
Fortify Your Career with a Master of Science from UF
Vitamins, drugs and other compounds can profoundly impact the major human body systems. We examine their beneficial and detrimental effects in the University of Florida’s online Master of Science in Medical Sciences with a concentration in Medical Physiology and Pharmacology, offered through our College of Medicine.
Built around an MCAT-aligned curriculum, our 30-credit MS program prepares you for medical school or nursing school admission and a variety of rewarding careers in medicine, science, pharmacy and research.
- Earn your master’s degree entirely online — no campus or lab visits required.
- Get started with no GRE requirement.
- Complete coursework at your own pace from practically any location.
- Maintain your professional commitments.
- Transfer up to 15 credits from a qualifying UF graduate certificate program.
- Finish your degree in as little as two semesters.
Add a respected master’s degree to your career credentials. Apply today!
Sources:
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/WYNTK-Consumer/
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/is-there-really-any-benefit-to-multivitamins
https://www.prevention.com/life/a20474960/how-to-make-sure-youre-benefiting-from-your-vitamins/
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/which-vitamins-should-you-take
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/7041-digestive-system
https://time.com/6171584/are-vitamins-supplements-healthy/
Drugs That Treat Multiple Conditions: Hydroxyzine
Throughout the pharmaceutical world, there are numerous drugs that help people manage multiple conditions. Topiramate, developed to treat seizures, doubles as a migraine treatment. Bupropion, typically prescribed as an antidepressant, also aids in smoking cessation. Minoxidil, developed to treat high blood pressure, is perhaps better known for reversing hair loss.
Clinical trials determine the effectiveness and safety of drugs before they’re approved for public use, but sometimes these trials reveal unforeseen benefits. Hydroxyzine is a prominent example of this type of versatile medication, and one we’ll explore its multiple uses in this article.
Hydroxyzine: A Versatile Medication
Hydroxyzine, a prescription antihistamine typically administered orally, has applications beyond stopping runny noses. As an antihistamine, hydroxyzine is commonly used as a treatment for allergies and allergic reactions, such as certain types of eczema, dermatitis, hay fever, asthma and conjunctivitis. Its additional uses include:
- Anxiety treatment
- Sedation before medical procedures
- Nausea and vomiting relief
- Motion sickness symptom alleviation
Some studies, including those conducted by UF Health, also suggest that the anti-inflammatory response of hydroxyzine lowers the risk of death among hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
How Hydroxyzine Works
Hydroxyzine, an H1-blocker, impedes the effects of histamine, a chemical produced within the human immune system. It crosses the blood-brain barrier and interacts with serotonin and dopamine receptors, producing sedative and anxiety-reducing effects.
H1-blockers such as hydroxyzine stop histamines from binding to histamine receptors, which can be found throughout the body, including on glandular and mast cells, smooth muscle, and nerves. Histamines widen blood vessels and make them more permeable, leading to fluid leakage from capillaries into adjacent tissues. H1-blockers prevent these actions, effectively reducing inflammation and alleviating allergy symptoms.
If an inflammatory condition leads to chronic inflammation, treatment is essential for the prevention of damage to organs and DNA and the development of several serious diseases, including cancer and heart disease.
Master Drug Mechanisms and Advance Your Medical Sciences Career
The University of Florida’s online Master of Science in Medical Sciences with a concentration in Medical Physiology and Pharmacology explores how various drugs and substances affect body systems and overall human health. Our 30-credit program enables you to gain crucial knowledge and a valued credential that can lead to a rewarding career as a:
- Physician
- Physician assistant
- Nurse
- Clinical scientist
- Professor
- Researcher
Our program’s MCAT-aligned curriculum helps prepare you for admission to medical school or nursing school and can distinguish you among a wide field of candidates in a highly competitive admissions environment where about 60% of medical school applicants are rejected annually.
Benefits of Online Learning
As an online student, you’ll complete your degree entirely online. No campus or lab visits are required. This empowers you to:
- Access coursework from practically anywhere.
- Work at your own pace.
- Connect with classmates and faculty anytime through email, discussion groups and other online tools.
- Network with students from the U.S. and around the world for broader career prospects.
- Earn a graduate credential while meeting your professional and personal obligations.
Start Sooner and Finish Faster
Our online master’s degree in medical physiology and pharmacology program does not require GRE scores, enabling you to bypass that common admission step. And you can collect your online master’s degree in medical physiology and pharmacology sooner — in as little as two semesters — if you’ve already completed a qualifying UF graduate certificate program. We allow you to transfer up to 15 credits to this MS program from your:
Choose an Institution Acclaimed for Quality
This master’s degree program is bolstered by UF’s exceptional reputation and accolades:
- Liaison Committee on Medical Education (LCME)-accredited College of Medicine
- Renowned faculty comprised of the same accomplished researchers and physicians who teach UF’s medical students
- Acknowledgements including:
Prime yourself for greater opportunities ahead. Apply now!
Sources:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/hydroxyzine-oral-route/description/drg-20311434
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/20775-hydroxyzine-solution
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/24854-histamine
https://health.usnews.com/wellness/slideshows/8-medications-that-treat-multiple-conditions?slide=9
https://www.aocd.org/page/antihistamines?
How Does Nicotine Replacement Therapy Relieve Addiction?
”From a scientific standpoint, nicotine is just as hard, or harder, to quit than heroin.” This jarring statement from nicotine researcher Dr. Neil Benowitz may explain why so many people struggle with giving up nicotine for years, or even a lifetime.
When individuals use conventional cigarettes, cigars, chewing tobacco or e-cigarettes, the bloodstream quickly absorbs the chemical nicotine and transports it to the brain. The brain responds by releasing dopamine, the “happy hormone,” producing a pleasurable sensation. The body eventually grows accustomed to that sensation and becomes dependent on nicotine to produce it. When a smoker quits cigarettes, they may begin to feel angrier, sadder and hungrier due to the lack of stimulation from nicotine. They start to crave that happy hormone feeling. This is nicotine addiction.
Viable Alternatives to Nicotine
Overcoming nicotine addiction is no easy task for many. But there are substitutes for nicotine that are designed to wean addicts off of this harmful substance. In 1984, nicotine addicts found a new hope as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved nicotine replacement therapy (NRT). NRT products were first introduced in the form of gum, then later patches, lozenges, inhalers and other methods. Many of these were originally offered by prescription only but subsequently became available over the counter.
NRTs act upon the receptors in the brain that are affected by nicotine, easing the cravings and withdrawal symptoms that most people who give up nicotine experience. Quite often, using multiple NRT methods at the same time yields better results. According to researchers, NRTs boost tobacco quit rates by up to 70%. In most cases, therapy involves gradually reducing the amount of nicotine and/or frequency of the use of NRT until the user is weaned off the addictive chemical altogether.
It should be noted that while many nicotine users are able to overcome their physiological dependence on nicotine through NRT, such products do not alleviate any behavioral associations that tobacco users develop. For example, some smokers associate pleasure with the act of picking up a cigarette and placing it in their mouth or just feeling the sensation of having a cigarette between the lips. For this reason, behavioral therapy is often recommended alongside or following NRT.
Master Physiology and Pharmacology Online
The University of Florida’s renowned College of Medicine provides degree and certificate programs that will help you understand how nicotine and other substances can impact human physiology and broaden your knowledge of body systems overall. Each of these programs is presented entirely online, which allows you to complete a respected education credential on your own schedule, around any professional and personal responsibilities you may have. All programs are available 24/7 from just about any location.
Master of Science in Medical Sciences with a concentration in Medical Physiology and Pharmacology
Our online master’s degree in medical physiology and pharmacology program explores the major human body systems and how different drugs impact and are impacted by them. In addition, our program helps you prepare for National Board, MCAT and other key exams that can enable you to advance into a new role in your medical career. You may be able to finish this program in as little as one year.
What’s more, if you have completed a Graduate Certificate in Medical Physiology or a Graduate Certificate in Medical Physiology with a specialization in Cardiovascular/Renal Physiology (more information below), you’re already halfway to earning a master’s degree in medical physiology and pharmacology. Our 30-credit degree program accepts up to 15 credits from these UF graduate certificate programs. Consider the advantages of our master’s degree in medical physiology and pharmacology program:
- Earn your master’s degree in as little as one year.
- Complete coursework at your own pace.
- Build clinical knowledge that can help you excel in medical school.
- Get started without taking the GRE.
- Use financial aid options, if needed.
- Add a career-defining education credential to your resume.
Graduate Certificate in Medical Physiology
Our Graduate Certificate in Medical Physiology investigates the fundamentals of the field and explores individual systems of the human body. You can take as many as six courses in this 9- to 14-credit program, though you are only required to complete 9 credits. That means you may be able to complete the program in a single semester.
Graduate Certificate in Medical Physiology with a specialization in Cardiovascular/Renal Physiology
We also offer a Graduate Certificate in Medical Physiology with a specialization in Cardiovascular/Renal Physiology, an advanced-level look at cardiovascular and renal physiology and pathophysiology that you’ll find invaluable in a clinical setting. You can complete this 12-credit program in as little as two semesters.
Find out how the human body functions and interacts with different drugs and other substances in an entirely online master’s degree or graduate certificate program from the University of Florida.
Sources:
https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/basics/dopamine
https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/tobacco-nicotine-e-cigarettes/nicotine-addictive
https://www.cancer.org/healthy/stay-away-from-tobacco/guide-quitting-smoking/nicotine-replacement-therapy.html
https://www.verywellmind.com/nicotine-replacement-therapy-4013217
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/08/160831085320.htm
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5003586/
https://www.healthline.com/health/oral-fixation#examples-in-adults
How This Program Helps Prepare You for Medical School
Medical school is a challenging but ultimately fulfilling endeavor for most students. Completing it positions you to make an immeasurable impact on the lives and health of others in a rewarding profession.
In recent years, however, about 60% of applicants have not been accepted into medical school — even as doctor shortages increase. In fact, some industry organizations have forecast a physician shortfall approaching 86,000 by 2036.
These figures underscore the importance of submitting a standout medical school application. Your application should clearly demonstrate that you not only meet the requirements but also possess the skills, credentials and determination needed to tackle the rigors of medical school and become an M.D.
The University of Florida’s College of Medicine offers an online Master of Science in Medical Sciences with a concentration in Medical Physiology and Pharmacology program that can set you up for success in the medical school application process and beyond. Here’s how this program can benefit you as an aspiring medical school student.
The Difference Our Degree Can Make
Our online master’s degree in medical physiology and pharmacology can help prepare you for medical school in several ways:
MCAT-Aligned Curriculum
Our program features curriculum designed to prepare you for the Medical College Admission Test (MCAT) — a key requirement for medical school admission. Through assignments and research on carefully selected topics, you’ll acquire a solid foundation for the exam. Numerous graduates have confirmed that our program provided excellent preparation for specific sections of the MCAT.
See course list and course descriptions here.
A Standout Credential That Demonstrates Your Dedication
Passing the MCAT is important, but is it enough? A master’s degree in medical physiology and pharmacology enhances your medical school application because it shows admissions committees your willingness to acquire advanced knowledge beyond the typical requirements. It can help you stand apart from that 60% of applicants who may not have a graduate credential and do not get accepted to medical school.
A Robust Program From a Respected University
A top-quality education is vital not only for catching the attention of a medical school admissions committees but also for thriving in medical school once you’re admitted. Built on more than 170 years of proven academic excellence, UF’s reputation for quality precedes it and is reflected in our regional accreditation, our graduates’ accomplishments and the accolades we regularly receive. Our 2024 acknowledgments include:
Recognized, Experienced Faculty
Our online master’s degree in medical physiology and pharmacology program is taught by the same College of Medicine professors, researchers and medical doctors who teach on campus. They understand your goals and are ready to help guide you toward them.
Comprehensive Preparation for Medical School
Combining two sciences into one unique master’s degree, this 30-credit online program is where you’ll :
- Gain in-depth scientific knowledge of essential human body systems.
- Examine how drugs interact with living organisms at the cellular and molecular levels.
- Study both healthy and diseased conditions within these systems.
Our program enables you to:
- Start with no GRE requirement.
- Complete coursework without any campus or lab visits.
- Finish in as little as two semesters.
- Earn your degree faster if you’ve previously completed one of these graduate certificate programs:
Stay Engaged Wherever You Are
Delivered in an entirely online asynchronous format, our program empowers you to complete your studies on a flexible schedule from any location that suits you. You don’t have to choose between your ongoing commitments and earning a degree that can elevate your academic and professional potential. Nor do you have to give up the connection that you expect from a university experience. You’ll interact with faculty and classmates via email, discussion groups and other online tools throughout our program.
Interested in gerontology? Our online master’s degree in medical physiology and aging provides another path to medical school and related careers. See details.
Medical school is a challenge that you’re capable of meeting. Prepare with a master’s degree in medical physiology and pharmacology from UF. Apply today!
Sources:
https://www.ama-assn.org/medical-students/preparing-medical-school/pre-med-frequently-asked-questions
https://www.usnews.com/education/best-graduate-schools/top-medical-schools/articles/why-its-still-hard-to-get-into-medical-school-despite-a-doctor-shortage
https://www.aamc.org/news/press-releases/new-aamc-report-shows-continuing-projected-physician-shortage
Becoming an Astronaut: How Space Flight Affects Our Bodies
As children, many of us shared a similar professional goal: We were determined to become astronauts. Little did we know that NASA’s acceptance rate is abysmally low. In 2024, more than 8,000 people applied to become astronauts. Of that number, NASA will only choose between eight and 12 candidates.
Beyond the rigorous selection process, one aspect of being an astronaut that we likely didn’t consider as children is the effect space flight has on our bodies. With drastic changes in gravity and no atmosphere to shield us from the sun’s UV rays, several short- and long-term changes can occur in our bodies while in space.
Settle in and buckle up as we explore the effects of space flight on humans and — for those still interested — the prerequisites for becoming an astronaut.
Immediate Effects During Launch
In addition to the adrenaline spike they may feel during the famed countdown to liftoff, astronauts may experience several other physiological changes during space shuttle launches due to increased G-forces, including:
- Difficulty moving limbs.
- Tunnel vision or brief loss of consciousness.
- A reduced ability for the heart to efficiently pump blood.
- Bodily fluids shifting upward, which can cause fluid retention in the upper body.
- Discomfort in the sinuses due to changes in air pressure.
Musculoskeletal Adaptations
If you’re on a commercial mission to space, you’ll likely only be there long enough to appreciate the beauty of Earth from above, notice its curvature and maybe even experience a few sunsets or sunrises, depending on your positioning. Astronauts on extended missions will remain in space much longer. The average duration of an astronaut’s mission aboard the International Space Station (ISS) is 6 months.
Half a year is plenty of time for the lack of gravity to take a toll on your musculoskeletal system (i.e., your muscles and bones). On Earth, your body constantly uses its muscles to resist the force of gravity. In space, however, there’s no gravity to fight, so you end up using your muscles significantly less.
Over time, living in a zero-gravity atmosphere can weaken your muscles and reduce bone mass. Fortunately, astronauts can mitigate the effects of these unique conditions before, during and after a mission by engaging in a rigorous exercise routine. During their time on the ISS, astronauts exercise for about two hours a day, strengthening their bodies by using a treadmill and incorporating strength training.
Changes to the Immune System
Having lived on Earth your entire life, your immune system has adapted to function under Earth’s gravitational pull. Experiencing altered gravity in space impairs your immune system’s peak performance. In addition to microgravity, increased radiation and disrupted circadian rhythms can also impact your immune system.
A weakened immune system might result in your body fighting harder and longer to combat an infection it could easily overcome on Earth. You might also become more susceptible to infections until you return to Earth’s normal conditions and your immune system readjusts.
Psychological and Cognitive Effects
Physical changes aren’t the only effects to expect while spending an extended period in space. Being away from family and in constant close quarters with the same small group of people for months can impact your mental well-being, leading to feelings of isolation or confinement.
Astronauts prepare for these psychological effects through several strategies, including:
- Undergoing psychological resilience training before the mission.
- Participating in simulated missions to acclimate to the cognitive demands of space travel.
- Establishing a structured daily routine while in space to maintain normalcy.
- Contacting family regularly via email and video calls.
- Bringing personal items and participating in group activities and hobbies aboard the ISS.
- Having regular check-ins and psychological assessments.
Do You Have What It Takes for a Trip to Space?
While astronauts face several mental and physical hurdles as they embark on expeditions in space, they’re also pioneering scientific research that could change the future of science, technology and the way we live. Although many people believe they have what it takes to become an astronaut, it requires more than just determination. In addition to being a U.S. citizen and having a minimum of three years of related professional experience, you need a master’s degree in a STEM field from an accredited institution.
Whether you aspire to become an astronaut or you’re interested in turning your fascination with the human body into a lucrative career, the University of Florida offers several online graduate programs ideal for those interested in advancing their careers in health and sciences:
Our online programs in medical physiology, offered by one of U.S. News’ top 50 national universities, also boast the following benefits:
- Affordable tuition rates.
- Year-round start dates.
- No GRE requirement.
- Flexible coursework completion on your timeline.
Take the first step in advancing your career in the expansive and profitable world of STEM — apply today!
Sources:
https://touroscholar.touro.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1077&context=sjlcas
https://www.kennedyspacecenter.com/blog/the-20-most-frequently-asked-questions-about-the-international-space-station
https://www.nasa.gov/missions/station/scientists-probe-how-long-term-spaceflight-alters-immunity/
https://www.abc.net.au/news/health/2024-03-09/preparing-human-mind-space-travel-mars-astronauts-mission/103563280
Comparing Graduate Credentials: Medical Physiology vs. Microbiology
If you’re considering a graduate credential, we salute you! The path to securing your dream position can be a long one, and a graduate certificate or master’s degree is often the first step in advancing your career, especially in STEM-related roles.
If you’ve narrowed down your graduate options to medical physiology and microbiology, it’s helpful to understand the similarities and differences between these fields. While these programs may share similar credit requirements and a strong foundation in fundamental biological concepts, they also have some distinct differences.
Let’s explore these differences and help you determine which program aligns best with your professional goals.
Program Curriculum
A significant difference between a graduate credential in medical physiology and one in microbiology lies in each program’s framework and content:
- Medical Physiology
If you’ve ever asked yourself, “Should I take anatomy and physiology for medical school?”, the answer is yes. Courses focused on anatomy and physiology provide essential knowledge that will help you succeed in medical and other professional schools. The University of Florida’s online MS in medical physiology and pharmacology program offers a broader application of biological sciences, integrating human and medical physiology into clinical settings. It also emphasizes key areas of pharmacology, preparing graduates for roles such as clinical research coordinator, medical educator or healthcare consultant.
- Microbiology
In contrast, a microbiology program concentrates more specifically on microorganisms and their effects on humans and the environment. Courses explore areas such as virology, infectious diseases and molecular genetics. The curriculum prepares graduates for diverse roles in research, diagnostics and public health.
Career Opportunities
Both graduate programs act as an excellent stepping stone toward numerous STEM-related careers. Below, we break down some of the specific careers available depending on the program you choose to pursue:
Medical Physiology
An MS in one of our medical sciences programs offers an excellent foundation for roles in the healthcare field, whether you’re interested in direct patient care, shaping public health policy, advancing biomedical research or teaching the next generation of medical professionals.
While some of these positions may require further education, our online graduate credentials in the medical sciences provide a strategic way to advance your journey toward the career you’ve always envisioned, in rewarding careers like:
- Clinical research coordinator
- Pharmaceutical sales representative
- Medical educator
- Surgeon
- Physician assistant
- Anesthesiologist
- Critical care nurse
- Pharmacist
- Biomedical research scientist
- Regulatory affairs specialist
Microbiology
As a graduate with an MS in microbiology, you’ll have the advanced skills needed to launch your career in a variety of in-demand roles in research and biotechnology, including:
- Biochemist
- Biophysicist
- Medical scientist
- Epidemiologist
- Molecular biologist
- Bioinformatics scientist
Job Outlook and Salary
The job outlook for STEM-related careers is projected to grow by 10.4% from 2022 to 2032, which is 6% higher than the national average for all occupations. Here are some projected job outlooks and salaries for different careers in each sector according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Medical Physiology
Registered nurses
- Median annual salary: $86,070
- Growth rate through 2033: 6%
Nurse Anesthetists
- Median annual salary: $129,480
- Growth rate through 2033: 40%
Physician assistants
- Median annual salary: $130,020
- Growth rate through 2033: 28%
Postsecondary teachers
- Median annual salary: $84,380
- Growth rate through 2033: 8%
Microbiology
Medical Scientists
- Median annual salary: $100,890
- Growth rate through 2033: 11%
Epidemiologists
- Median annual salary: $81,390
- Growth rate through 2033: 19%
Biochemists
- Median annual salary: $107,460
- Growth rate through 2033: 9%
Impact on Patient Outcomes
Envision yourself in a patient care role. Do you see yourself working one-on-one with patients, delivering personalized care tailored to their specific needs? Or would you prefer to make a broader impact, using your expertise to advance the understanding of diseases from the comfort of a lab coat?
A graduate degree in medical physiology offers a versatile entryway to several careers centered around patient care, whether you want to specialize in a particular area of medicine or take on a broader clinical role. However, if you’d rather step away from patient care and focus on other areas of medical sciences, there are plenty of roles that allow you to contribute to healthcare without direct patient interaction.
In contrast, a master’s degree in microbiology is ideal for those who wish to improve specific areas of health, such as food safety and public health. While these roles don’t often involve direct patient interaction, they offer opportunities to work in various settings, such as research laboratories, government agencies and pharmaceutical companies.
Earn a Graduate Credential in Medical Sciences From the University of Florida
A graduate credential in medical physiology or microbiology offers numerous benefits, bringing you closer to advancing your career and acquiring essential skills along the way. With a medical sciences graduate credential from UF, you’ll gain a strong foundation tailored to your chosen role. Our programs prepare you for professional school, demonstrating your commitment to your field and enhancing your application to admissions committees.
We offer seven unique, entirely online graduate programs in the medical sciences:
Many of our online students are already balancing busy professional and personal lives. We aim to help you maintain that work-life balance by offering all asynchronous courses. This flexibility allows you to complete your studies at your convenience — in as little as one year.
Jump-start your career in medical sciences with experienced professors from one of U.S. News’ top 50 universities in the nation. Apply to secure your spot next semester!
Sources:
https://www.bls.gov/emp/tables/stem-employment.htm
https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/registered-nurses.htm
https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/nurse-anesthetists-nurse-midwives-and-nurse-practitioners.htm
https://www.bls.gov/ooh/healthcare/physician-assistants.htm
https://www.bls.gov/ooh/education-training-and-library/postsecondary-teachers.htm
https://www.bls.gov/ooh/life-physical-and-social-science/medical-scientists.htm
https://www.bls.gov/ooh/life-physical-and-social-science/epidemiologists.htm
Sleep Physiology: The Restorative Power of Rest
We spend about one-third of our lives asleep, making it no surprise that sleep is a favorite activity for many. Yet, few of us consider the internal processes at work as we settle into bed and drift into dreamland.
This is where sleep physiology comes into play. It delves into the biological processes behind sleep, exploring how our bodies regulate it, its effects on bodily functions and the different stages of sleep.
So, grab your favorite pillow and join us as we uncover the essentials of sleep physiology and discover how to enhance your sleep habits for optimal rest and renewal.
The Sleep Cycle
Each night, we cycle through two primary phases of sleep:
- Nonrapid Eye Movement (NREM)
NREM sleep accounts for approximately 75% of your sleep time and consists of three stages:- Stage one: This brief phase occurs as you start to fall asleep and lasts about five minutes.
- Stage two: After we nod off, we enter a light sleep for around 25 minutes.
- Stage three: This is the deepest phase of NREM and often the hardest to wake from. Waking up during this phase can lead to mental fogginess and reduced performance for up to an hour. It is also the most restorative phase, where the body repairs tissues and boosts the immune system.
- Rapid Eye Movement (REM)
Following NREM, REM sleep begins with rapid eye movements and accounts for about 25% of your total sleep time. This phase is famous for creating vivid dreams — like that one where your cat juggled baby mice before a crowd of elderly lions in 1980s punk rock gear. Despite its rich dream content, REM sleep is the least restorative phase.
Throughout the night, we cycle through these two phases, with the first NREM cycle lasting about 70 minutes and lengthening with each subsequent cycle. The initial REM cycle lasts around 10 minutes, with later cycles extending up to an hour. In total, we experience approximately four to six sleep cycles a night.
Effects of Impaired Sleep
Have you ever struggled through a few rough nights of sleep? Whether it’s due to caring for a new baby or giving in to that third cup of coffee, various factors can lead to restless nights.
You might have noticed the effects of impaired sleep, like difficulty retaining new information, decreased coordination or mood swings. If so, you’re not alone. According to the National Council on Aging, 30% of Americans suffer from insomnia, and 10% say it affects their daily lives.
Psychological risks of continued poor sleep may include:
- Hallucinations
- Mania
- Impulsive behavior
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Paranoia
- Suicidal thoughts
The Benefits of Restorative Rest
We’ve all experienced waking up from a blissful eight (or even ten) hours of solid sleep. On those mornings, we often feel well-rested, with increased mental clarity, heightened energy and a renewed drive to tackle the day. Oh, the power of a good night’s sleep.
While sleep needs vary based on genetics, adults aged 18 to 60 generally require seven or more hours each night to experience the following benefits:
- Improved immune response
- Reduced stress levels
- Enhanced metabolism
- Better heart health
- Lower risk of chronic conditions, such as Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure and stroke
- Improved attention span
- Greater ability to remember information
Tips for Optimizing Sleep
Even under the best circumstances, not every night will provide the perfect amount of zzz’s — but you can still significantly increase the number of nights you enjoy rejuvenating rest. Here are some tips to improve the quality of your sleep:
- Establish a bedtime routine
Go to bed at the same time each night. Develop a consistent pre-sleep routine, such as showering, brushing your teeth and reading a book in bed, to help you wind down and prepare for rest.
- Maintain a sleep-positive environment
Minimize auditory distractions by closing the door or using a sound machine. Maintain a cool room temperature to enhance thermoregulation, which may help you remain in REM sleep for longer periods.
- Turn off electronic devices before bed
While scrolling through social media or catching up on news might seem like a relaxing end to your day, the blue light emitted by phones can interfere with sleep. Instead, replace screen time with relaxing activities like journaling, meditating, stretching or reading.
Turn Your Passion Into a Rewarding Career
If you’re intrigued by what your brain and body are up to while you sleep, or if you’re considering a career dedicated to improving the sleep health of others, there are several paths to explore within this segment of the healthcare industry.
The University of Florida offers a variety of online graduate programs in the medical sciences designed to help you achieve your professional goals. These programs provide an excellent foundation, whether you’re ready to enter the workforce or plan to apply to professional school for further education.
Explore the online graduate certificates and master’s degrees below to find the program that best suits your interests and career aspirations.
Benefits of earning a graduate credential with UF include:
- Earning many of these credentials in as little as one year.
- Completing the program at your own pace.
- Working on assignments from anywhere, anytime.
- Applying without GRE scores required.
- Enrolling in programs with year-round admission.
- Receiving an education from one of U.S. News’ top 50 national universities.
With so many online graduate credentials to choose from, the choice is yours. Which program aligns with the future of your dreams? Apply today!
Sources:
https://www.healthline.com/health/sleep-deprivation/effects-on-body#effects
https://www.ncoa.org/adviser/sleep/sleep-statistics/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526132/
https://www.cdc.gov/sleep/about/index.html
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/what-is-the-ideal-sleeping-temperature-for-my-bedroom
https://www.sleepfoundation.org/how-sleep-works/how-electronics-affect-sleep
Gut Flora 101: Key Functions of Gut Bacteria and Health Tips
This very second, you have trillions of microorganisms living inside your body — so many that they make up one to three percent of your entire body weight! While you have a sizable combination of bacteria, fungi and viruses swarming around inside you, most microbial cells in your body consist of different types of bacteria, many of them residing in your gut.
All those gut bacteria have a handful of important jobs to do, including protecting you against pathogens and helping you digest food, which can be especially helpful if you got a little too excited at the all-you-can-eat pizzeria last weekend. Prepare to thank all those tiny bacteria for their hard work as we discuss the important functions that gut bacteria play in our everyday lives and review some tips to help you improve your gut flora.
What Is Gut Bacteria?
While you have microbes living on your skin and throughout your body, most of them are bacteria that live in your large intestine, small intestine and stomach. Also known as gut bacteria, this gargantuan number of tiny organisms goes by several other names as well, including:
- Microflora
- Microbiome
- Microbiota
- Intestinal flora
- Gut flora
Regardless of which moniker you use, they all refer to approximately 1,000 species of bacteria that populate your gut, each responsible for various roles in your body. But you’re not born with all these microbes in your body. A baby in utero has an almost entirely sterile gut. It’s not until they make their way through the birth canal that they receive the mother’s vaginal bacteria. While this might not sound glamorous, it’s exactly what a baby needs to begin forming a healthy gut microbiome.
What Are the Functions of Gut Bacteria?
In recent years, microbiologists have spent an increasing amount of time determining the role that intestinal flora play in our health. With so many bacteria inside our intestines, it only makes sense that they are somehow significant, right?
Scientific research shows that gut bacteria may be responsible for multiple roles in our bodies, including the ones listed below.
Digesting Food
Some of the first bacteria that babies grow in their gut are called Bifidobacteria. This type of microbe helps us digest the healthy sugars found in breast milk and promotes growth. As our gut flora become more advanced, they help us digest other forms of nutrients too, including:
- Fiber
- Complex carbohydrates (like whole grains and vegetables)
- Proteins
- Vitamin K
Supporting Your Immune System
Some of the bacteria in your gut help line your large intestines to keep harmful substances — and leaky gut syndrome — at bay. Helpful bacteria may also work in tandem with your immune system to help fight against pathogen-causing bacteria and communicate with immune cells to control how your body reacts to infection.
Influencing Brain Function
Have you ever experienced a case of “the butterflies” in your stomach before a big test or a nerve-wracking first date? According to the American Psychological Association, your gut is tied to your mood, ability to learn, memory and emotions. So, when you find yourself “going with your gut,” it might be because you’re using your second brain — a.k.a. your gut bacteria’s independent nervous system — to help you make some of your decisions.
In addition, your brain and gut are connected through neurotransmitters. Often produced in your brain, these chemicals are responsible for controlling your feelings and emotions. For example, serotonin is a neurotransmitter that provides feelings of happiness. Not to be outdone, your gut also produces serotonin as well as gamma-aminobutyric acids (GABA), which help regulate negative emotions like anxiety or fear.
Does Gut Bacteria Also Cause Health Issues?
Yes, maintaining an unhealthy diet and not getting adequate sleep increases your risk of altering your gut flora’s composition. If you find yourself with an imbalance of the healthy microbes in the gut, it may contribute to certain health problems, such as:
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Inflammatory bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Metabolic syndrome
How to Improve Gut Flora: Quick Tips
If you find yourself with more harmful than healthy bacteria, there is a light at the end of the tunnel. With a few changes to your diet, you can begin rebuilding the healthy bacteria in your microbiome. Below are a few tips to implement to get your gut health back on track:
- Eat a healthy combination of macronutrients such as complex carbs, healthy fats and lean protein.
- Opt for fermented foods like yogurt, sauerkraut and kimchi. They all contain the healthy bacteria Lactobacilli, which may lessen disease-causing bacteria in the gut.
- Incorporate prebiotic foods like artichokes, asparagus, oats and bananas. They stimulate the growth of healthy gut bacteria.
- Only take antibiotics when necessary. While they work to kill bacteria-causing infections in your body, they also kill good bacteria.
You’re not the only one who takes gut health seriously — so does the University of Florida. Our online graduate certificate programs allow you to develop an in-depth comprehension and mastery of the fundamental concepts in several areas of medical sciences, preparing you for numerous careers in healthcare, education, public health and more.
In addition to acquiring the skills that will provide a leg up against the competition, our 12-credit certificate offers multiple benefits for working professionals, including:
- Entirely online courses
- Classes available year-round
- No GRE requirement
- Affordable tuition
Apply to the program that aligns with your future plans today.
Sources:
https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-human-microbiome-project-defines-normal-bacterial-makeup-body
https://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/the-secret-world-inside-you/microbiome-at-birth
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/gut-microbiome-and-health#TOC_TITLE_HDR_2
https://microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40168-019-0704-8
https://www.apa.org/monitor/2012/09/gut-feeling
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/gut-brain-connection
https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-are-your-gut-flora-1944914
How Does Ozempic Work for Diabetes? A Complete Breakdown
In the United States, approximately 38 million people have diabetes. Within that population, about 95% have type 2 diabetes, a condition that affects your body’s ability to metabolize sugar, otherwise known as glucose.
One such medication is Ozempic, an injectable drug approved by the FDA in 2017 to improve blood sugar control in adults with type 2 diabetes. Since its introduction, Ozempic has become widely used—not only for its ability to lower blood sugar but also for a notable side effect: weight loss. While Ozempic is not FDA-approved for weight management, its impact on appetite and metabolism has drawn attention beyond the diabetes community.
In this article, we’ll explore how Ozempic works, its role in diabetes management, and why it has gained so much popularity.
What Is Ozempic — and What Does It Treat?
Ozempic is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It works by improving blood sugar levels over the long term, which is measured by reducing a person’s HbA1c (hemoglobin A1c) levels. Additionally, regular use of Ozempic may help lower the risk of major cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes in individuals with type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
How Does Ozempic Work?
The active ingredient in Ozempic, semaglutide, works by mimicking a hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). When it activates the GLP-1 receptors, Ozempic enhances your body’s ability to control blood sugar by:
- Telling your pancreas to release insulin when blood sugar is high
- Blocking the release of a hormone called glucagon, which can make your liver release extra sugar into your blood
- Slowing down the rate at which food moves through your intestines, lowering the amount of sugar that enters your bloodstream after you eat
- Making you feel full, leading to less food consumption
Is Ozempic a Weight Loss Aid?
In short, no — although one of the common side effects of Ozempic is its ability to help some users lose weight. In a recent Forbes article, Dr. Christopher McGowan explained that in addition to Ozempic’s effects on blood glucose, the active ingredient, semaglutide, also impacts the hunger centers in the brain, reducing feelings of hunger and food cravings.
While not approved by the FDA as a weight-loss medication, its sister drug, Wegovy, received approval for use by overweight individuals or those with cardiovascular disease in 2021. The key difference between Ozempic and Wegovy is the dosage, with Wegovy offering a higher dose of semaglutide to aid weight loss (alongside a healthy diet and exercise).
So, although the main function of Ozempic isn’t to help people lose weight, its inclusion of semaglutide often results in weight loss as a side effect experienced by many users. Because type 2 diabetes is often associated with obesity, its potential to assist in weight loss may also help individuals manage their condition more effectively and improve their overall health.
Amp Up Your Career in Medicine with a Graduate Credential from UF
Whether you’re interested in a career in drug development or sales and marketing, the University of Florida offers an online master’s degree in medical physiology and pharmacology tailored to helping you achieve your goals in the medical industry.
This entirely online program, developed by two renowned departments at UF, consists of 30 credits divided into two core areas, each comprising 15 credits. The program aims to provide you with an advanced scientific understanding of medical physiology, which focuses on the major human body systems, and medical pharmacology, which examines the impact of drugs on living organisms at the cellular and molecular levels.
With asynchronous courses, you can complete coursework on a timeline that coordinates with your busy schedule, finishing the program in as little as two semesters.
If you’re curious about some of our other medical physiology programs, we have several other specialized programs, depending on your interests and career aspirations, including:
- Master’s Degree in Medical Physiology and Aging
- Graduate Certificate in Medical Physiology
- Graduate Certificate in Medical Physiology with a specialization in Cardiovascular/Renal Physiology
If you have questions about any of our programs, please don’t hesitate to contact us for more information. And when you’re ready to make the first move toward making your career dreams a reality, the application is only a click away.
Sources:
https://www.fda.gov/drugs/postmarket-drug-safety-information-patients-and-providers/medications-containing-semaglutide-marketed-type-2-diabetes-or-weight-loss
https://www.ozempic.com/why-ozempic/how-ozempic-works.html
https://www.forbes.com/health/weight-loss/ozempic-for-weight-loss/
https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-treatment-reduce-risk-serious-heart-problems-specifically-adults-obesity-or
What Is Ebola — and How Does It Affect Your Body?
In 1976, researchers first identified a frightening virus that had emerged in the African nation then known as Zaire. While the source of this fast-moving, destructive disease remains unknown, Ebola is believed to have spread to humans from apes, monkeys and bats. There have been several Ebola outbreaks since 1976, primarily in African countries, though the disease has been found in animals originating from Asia as well.
More recently, the most consequential outbreak became a worldwide epidemic: Beginning in Guinea in 2013, the disease spread to other West African countries and later Europe, the United Kingdom and the United States. In the period of two and a half years, Ebola was responsible for killing more than 11,000 people.
In this article, we explore the devastating effects of the Ebola virus on the human body, tracing its progression from initial symptoms to immune system disruption and organ failure.
What Is Ebola?
Ebola is a severe and often fatal disease caused by the Ebola virus. Viewed through a microscope, Ebola looks somewhat like a worm that’s knotted and looped at one end. Like many diseases, it may not be easily recognized by its symptoms, since it shares early symptoms common in many other diseases, including those that indicate a far less serious condition. These symptoms may appear up to three weeks after exposure to the virus and include:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Aches
- Fatigue
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Unusual bruising
- Bleeding from multiple orifices
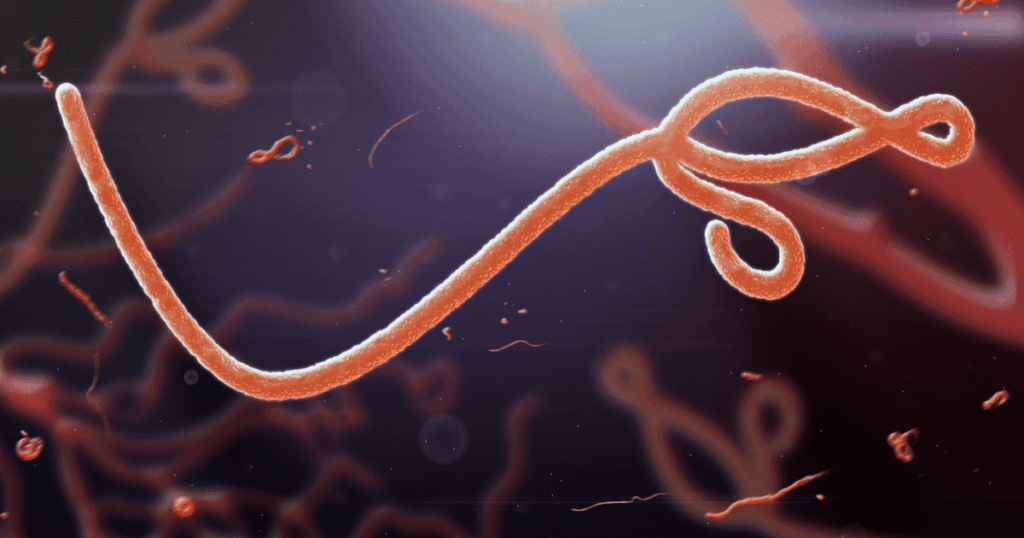
How Is Ebola Transmitted?
Humans can contract the virus through contact with infected animal blood and tissue, often via hunting and eating carriers of the disease or being bitten by one of them. The infected individual may then expose others to the disease through their bodily fluids, which can enter the body through a wound, the mucous membranes of the face, or intimate contact. Even a person who has died from Ebola can remain contagious, so their bodies must be handled with care.
What Does Ebola Do Once Inside the Body?
Ebola immediately attacks the immune system that was designed to fight it, leaving immune cells unresponsive, then rapidly replicates itself and spreads through the bloodstream. Other infected immune cells throughout the body cause clots that rob organs of essential blood. The virus does some of its most catastrophic damage by inhibiting plasma production, though other organs and systems are also impacted as the disease makes its way through the body.
Many patients die from Ebola: up to 90%, with an average of 50%. Having quality medical care and a strong immune system can increase one’s odds of recovery. End-stage symptoms may include brain inflammation and organ failure. Medical experts believe that Ebola survivors may develop some immunity, as antibodies stay in their blood for up to a decade.
Discover How Disease and Other Factors Affect Our Body Systems
As you’ve seen, Ebola can wreak havoc throughout the body, impacting many organs and often resulting in death. The University of Florida is proud to offer several entirely online Master of Science programs that provide different perspectives on the body systems, their organs and factors that can affect them. Some of them include:
Master of Science in Medical Sciences with a concentration in Medical Physiology and Pharmacology
Acquire a comprehensive scientific understanding of key human body systems, delve into the effects of drugs on living organisms at cellular and molecular tiers, and explore both normal and abnormal conditions in human body systems. Finish this 30-credit degree program in as little as two semesters.
Master of Science in Medical Sciences with a concentration in Medical Physiology and Aging
Develop a more expansive and profound understanding of the biological processes associated with aging. Finish this 30-credit degree program in as little as one year.
Bring the benefits of a master’s degree in medical physiology to your career!
Sources:
https://time.com/3502740/ebola-virus-1976/
https://www.itg.be/en/health-stories/impact-stories/the-discovery-of-and-research-on-the-ebola-virus



